How to use with NW.js
This guide shows how to use Socket.IO within a NW.js (previously known as node-webkit) application.
Usage
By default, NW.js creates two different JavaScript contexts:
- a browser context, which has access to the Web API (one context per window/frame)
- a Node context, which has access to the Node.js API (shared between all windows/frames)
Reference: https://nwjs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/For%20Users/Advanced/JavaScript%20Contexts%20in%20NW.js/
The Socket.IO client can be created in both context, depending on your use case.
Browser context
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<body>
<p>Status: <span id="status"></span></p>
<p>Transport: <span id="transport"></span></p>
<!-- from the socket.io-client package -->
<script src="./node_modules/socket.io-client/dist/socket.io.min.js"></script>
<!-- or from a CDN -->
<!--<script src="https://cdn.socket.io/4.7.5/socket.io.js"></script>-->
<script>
const socket = io("http://localhost:3000");
const statusSpan = document.getElementById("status");
const transportSpan = document.getElementById("transport");
statusSpan.innerText = "Disconnected";
transportSpan.innerText = "N/A";
socket.on("connect", () => {
statusSpan.innerText = "Connected";
transportSpan.innerText = socket.io.engine.transport.name;
socket.io.engine.on("upgrade", (transport) => {
transportSpan.innerText = transport.name;
});
console.log(`connect ${socket.id}`);
});
socket.on("connect_error", (err) => {
console.log(`connect_error due to ${err.message}`);
});
socket.on("disconnect", (reason) => {
statusSpan.innerText = "Disconnected";
transportSpan.innerText = "N/A";
console.log(`disconnect due to ${reason}`);
});
socket.emit("hello", "world");
</script>
</body>
</html>
In that case, the Socket.IO client will use the WebSocket object provided by the browser.
Pros
- the Socket.IO connection can be debugged in the DevTools:
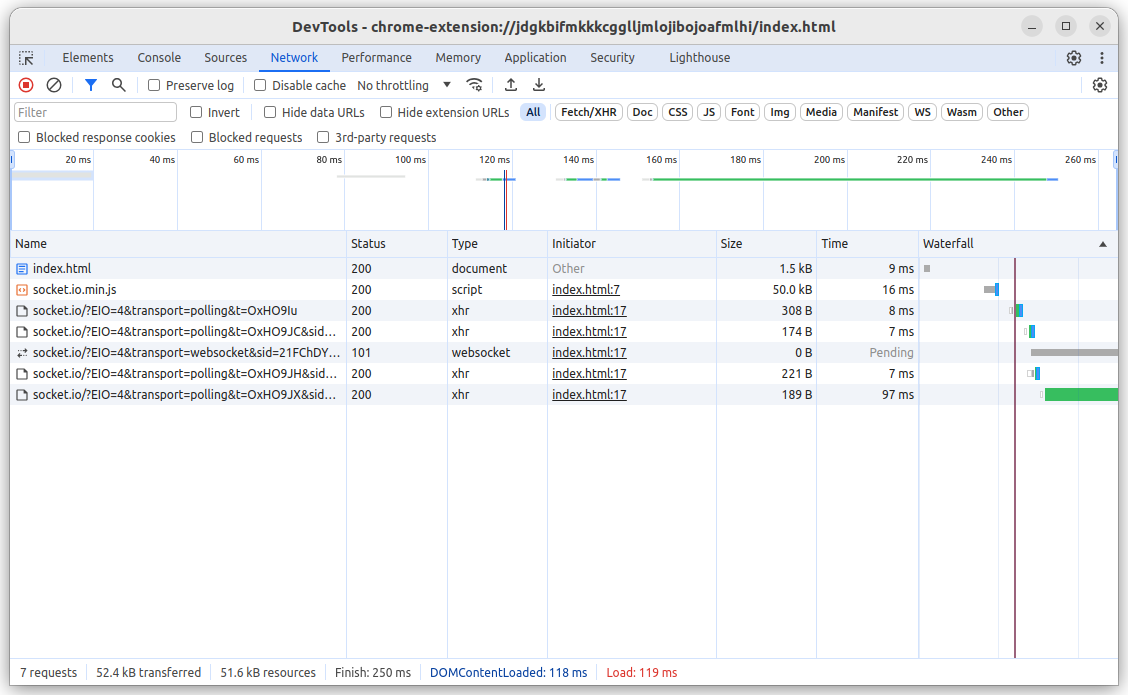
Cons
- the
extraHeadersoption will be ignored when using WebSocket only:
const socket = io("http://localhost:3000", {
transports: ["websocket"],
extraHeaders: {
"my-custom-header": "1234" // ignored
}
});
Node context
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<body>
<p>Status: <span id="status"></span></p>
<p>Transport: <span id="transport"></span></p>
<script>
const statusSpan = document.getElementById("status");
const transportSpan = document.getElementById("transport");
const { registerListeners, emit } = require("./socket");
registerListeners({ statusSpan, transportSpan });
emit("hello", "world");
</script>
</body>
</html>
const { io } = require("socket.io-client");
const socket = io("http://localhost:3000");
exports.registerListeners = function ({ statusSpan, transportSpan }) {
statusSpan.innerText = "Disconnected";
transportSpan.innerText = "N/A";
function onConnect() {
statusSpan.innerText = "Connected";
transportSpan.innerText = socket.io.engine.transport.name;
socket.io.engine.on("upgrade", (transport) => {
transportSpan.innerText = transport.name;
});
console.log(`connect ${socket.id}`);
}
if (socket.connected) {
onConnect();
}
socket.on("connect", onConnect);
socket.on("connect_error", (err) => {
console.log(`connect_error due to ${err.message}`);
});
socket.on("disconnect", (reason) => {
statusSpan.innerText = "Disconnected";
transportSpan.innerText = "N/A";
console.log(`disconnect due to ${reason}`);
});
}
exports.emit = function (...args) {
socket.emit(...args);
}
In that case, the Socket.IO client will use the WebSocket object provided by the ws package.
Pros
the Socket.IO connection will be shared between the different windows of your application
the client supports additional options specific to Node.js such as
agent,caorcert
const socket = io("https://localhost:3000", {
ca: fs.readFileSync("cert.pem")
});
- the
extraHeadersoption will properly be sent when using WebSocket only:
const socket = io("http://localhost:3000", {
transports: ["websocket"],
extraHeaders: {
"my-custom-header": "1234"
}
});
Cons
- the Socket.IO connection cannot be debugged in the DevTools (even when choosing "Inspect Background Page")
Sample project
https://github.com/socketio/socket.io/tree/main/examples/nwjs-example
That's all folks, thanks for reading!